How long should I wait?
As fertility declines with age, your biological clock is the most important factor to consider.
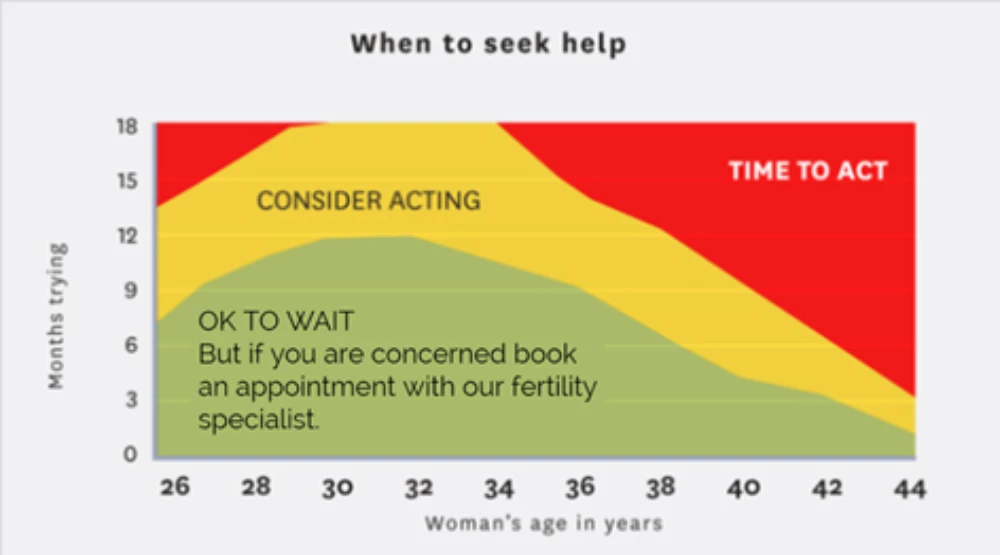
The graph below shows the recommended time frames for trying to conceive naturally before seeking help. For example, if you are 39 years old you should consider seeking help after 5 months and should be seeking advice after 1 year.
For more information about fertility and the biological clock, visit our ‘How age affects fertility’ page.
When to seek advice early
- If you have polycystic ovaries, endometriosis, or have been through a cancer diagnosis; we recommend you get in touch quickly so we can talk you through all your options and give you the greatest possible chance of success.
- If you’re a single woman considering motherhood in the future; it’s best to approach us early and consider egg freezing as this can be an option for you while you have a higher ovarian reserve and healthier eggs.
Medical History Review
In the Fertility Assessment - we will review any existing medical conditions, gynecological history, and any known problems, such as:
- Endometriosis
- Menstrual disturbance
- Ovulatory irregularities
- Menstrual cycle
- Past pelvic surgery
- Presence of pelvic pain
- Difficulties with intercourse
- Any symptoms suggestive of other medical conditions
If you’ve had fertility treatment before, it is important we review the records of previous treatments and investigations.
Physical Examination
- Body Mass Index: We’ll check your height and weight to calculate your BMI. BMI impacts fertility in different ways. If it’s too high or too low, it may influence your ability to conceive.
- For Men: It is rarely necessary to examine men unless the semen analysis is abnormal. Examination concentrates on detecting small volume testicles or a condition called varicocele, where dilated testicular blood vessels lead to overheating of the testicles.
Semen Analysis
Semen analysis is an essential part of fertility testing. Semen is analysed under a microscope for abnormalities in sperm concentration (count), motility (movement) and morphology (appearance).
Transvaginal Pelvic Ultrasound Scan & SonoHSG
- An assessment of your womb, ovaries, and fallopian tubes by ultrasound will be performed to check for anything that could be preventing conception and implantation.
- We check the shape, size, and regularity of the womb, as well as the appearance of the ovaries and the number of potential eggs that are available.
- SonoHSG is a simple outpatient examination to assess the patency of the Fallopian tubes which involves instillation of a special solution to outline the womb cavity and fallopian tubes.
Blood Tests
- Basic blood and infectious diseases test would be needed for both spouses. This includes a full blood count, blood group, venereal diseases, HIV, hepatitis and for women, rubella.
- Other blood tests can include a full hormonal profile which tests Follicular Stimulation Hormone (FSH), Luteinising Hormone (LH), Prolactin, Oestradiol levels. This isn’t necessary for women with regular menstrual cycles.
- For couples with recurrent pregnancy losses or IVF failures, it may be necessary to screen your chromosome make-up (carrier screening) and immune system (antiphospholipid syndrome screen).
- For women, a blood test called Anti Mullerian Hormone (AMH) is performed. This is the most accurate test available at the moment to assess ovarian reserve and to predicate the type of stimulation protocol needed for IVF.
Fertility Profiling
As fertility declines with age, Fertility Profiling gives you the information you need to protect your fertility and plan for the future.
Whether you are planning to have a family now or in the next few years, you may want to check the status of your fertility health and potential.
Fertility profiling identifies any potential health problems that may impact your fertility. It also tests for hereditary diseases and infections that can be passed on to your children.
The tests include a screening of egg reserves to estimate the likely number of fertile years left to conceive, as well as blood tests, semen analysis, an ultrasound, and a review of hormonal health.
We also offer genetic testing to screen for genetic conditions or chromosomal abnormalities that can affect your ability to conceive or have a healthy baby.


